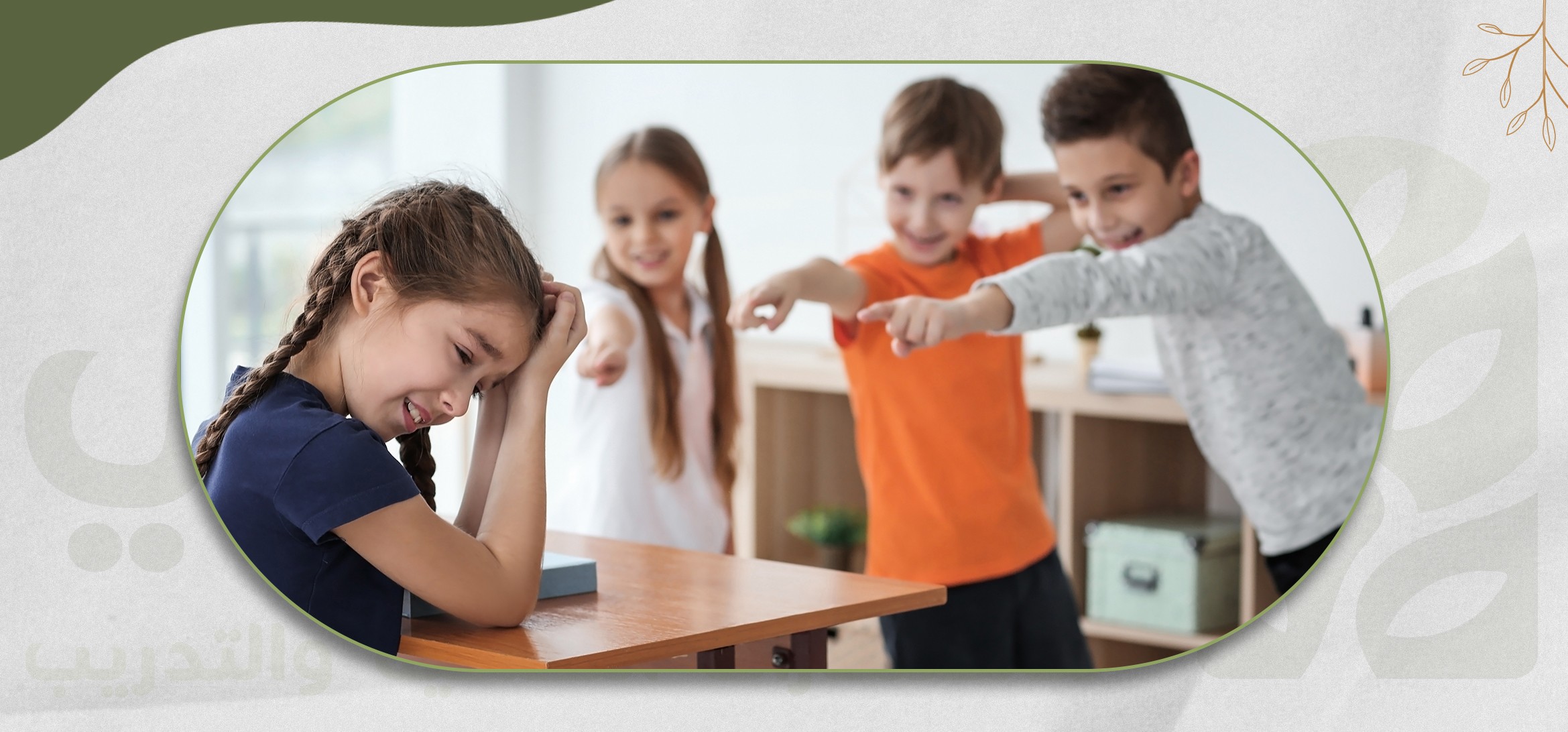
Bullying is not just aggressive behavior; it is a hidden weapon that destroys self-confidence and leaves deep emotional scars on those who experience it.
It reflects an inner weakness in the bully, even if they appear strong on the outside. Every act of bullying carries a message of pain and insecurity, making the world a harsher place and leaving a lasting impact that can persist throughout a person's life.
What are the types of bullying?
1- Verbal Bullying:
(Insults, using degrading or hurtful language, racial or religious slurs, sexist remarks, threats, and intimidation.)
2- Emotional/Social Bullying:
(Damaging friendships, excluding someone from a group, hurting a person’s reputation, spreading rumors within peer groups.)
3- Cyberbullying:
(Bullying through electronic devices such as smartphones, computers, and tablets.)
4- Physical Bullying:
(Hitting, restraining, spitting, sexual harassment, and physical assault.)
What is bullying?
Bullying is a form of violence committed by a child or a group of children against another child, where the target is deliberately and repeatedly hurt or harassed. Bullying can take many forms, such as spreading rumors, threats, physical or verbal attacks, intentional exclusion, or other subtle and harmful behaviors.
What are the signs your child may be experiencing peer bullying?
- Behavioral and Mood Changes:
-
Becoming more withdrawn or shy
-
Losing interest in previously enjoyed activities
-
Noticeable mood swings such as anxiety or depression
- Academic Changes:
-
Declining performance in school
-
Avoiding school or making excuses not to attend
-
Difficulty concentrating in class
- Physical Signs:
-
Unexplained bruises or injuries
-
Frequently lost or damaged personal items
-
Sleep disturbances, such as insomnia or recurring nightmares
-
Complaints of unexplained physical ailments
- Social Changes:
-
Losing friends or avoiding social activities
-
Limited interaction with peers or fear of attending social events
- Eating Habits:
-
Loss of appetite or overeating due to stress
- Technology Use:
-
Hesitation or reluctance to use a phone or computer, especially if they previously enjoyed doing so
-
Showing signs of sadness or anxiety after being online
What to do if your child is being bullied or witnesses bullying:
-
Listen openly and calmly to the child who is experiencing bullying.
-
Focus on making them feel supported and understood instead of jumping to conclusions or solutions.
-
Reassure them that they are not to blame for what happened.
-
Reinforce the child’s self-esteem and emotional strength, and help them regain confidence.
-
Communicate with the teacher or school about your concerns—the school plays an important role in stopping and preventing bullying.
-
Establish a trusting relationship with your child, so they feel comfortable coming to you with what’s troubling them.
Prevention and Empowerment:
The best approach is prevention—talk to your children before bullying happens.
Teach them about bullying and how to respond, and encourage them to turn to you or a teacher if they experience or witness it.
Let your child know they have an important role in reducing bullying—when they see a peer being bullied, they should support that peer and never stand by silently.
Bullying and violence can continue unless each child takes a stand, supports their peers, and reports what’s happening to adults.
Together, we can create safer, kinder environments where every child feels seen, supported, and strong.